Blockchain technology, once synonymous with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, has evolved into a transformative force across various sectors. Its decentralized nature, coupled with transparency and security, is reshaping industries such as supply chain management, healthcare, and governance. This article delves into how blockchain is revolutionizing these fields, providing real-world examples and insights.
1. Revolutionizing Supply Chains: Transparency and Efficiency
Supply chains are the backbone of global trade, yet they often suffer from inefficiencies, fraud, and lack of transparency. Blockchain addresses these challenges by providing a decentralized ledger that records every transaction in a secure and immutable manner.
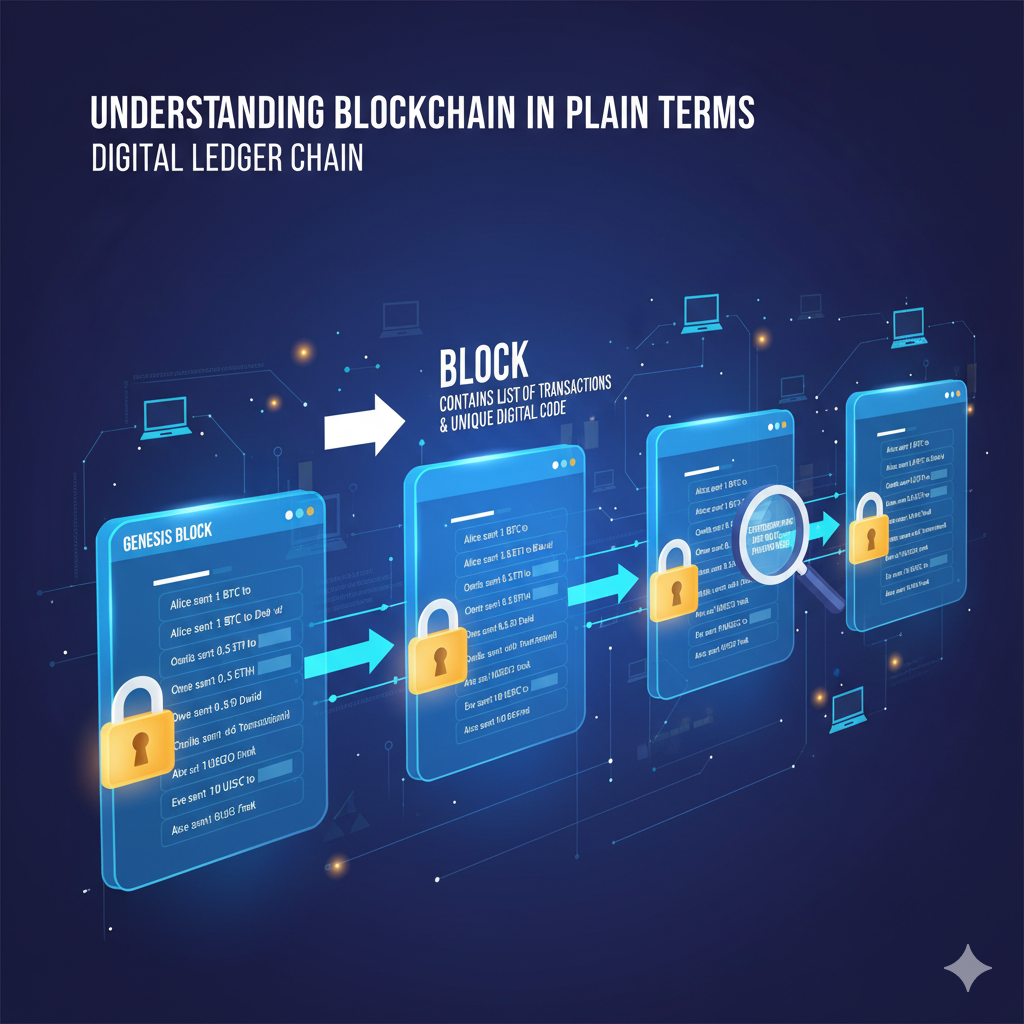
Key Benefits:
- Enhanced Traceability: Blockchain allows for real-time tracking of goods from origin to destination, ensuring authenticity and reducing fraud.
- Reduced Fraud and Errors: The immutable nature of blockchain records makes it difficult to alter transaction histories, thereby minimizing errors and fraudulent activities.
- Improved Efficiency: Automation through smart contracts streamlines processes, reducing delays and administrative overhead.
Real-World Example:
VeChain, a blockchain platform, has partnered with companies like PwC and Renault to enhance supply chain transparency. By using blockchain, these companies can verify the authenticity of products and ensure compliance with regulations, thereby building trust with consumers Investopedia.
2. Transforming Healthcare: Secure and Interoperable Systems
The healthcare industry grapples with issues like data fragmentation, security breaches, and inefficiencies in patient care. Blockchain offers solutions by providing a secure, decentralized system for managing health records and transactions.
Key Benefits:
- Data Security and Privacy: Blockchain ensures that patient data is encrypted and accessible only to authorized individuals, reducing the risk of breaches.
- Interoperability: Different healthcare providers can access and share patient data seamlessly, improving coordination and care.
- Supply Chain Integrity: Blockchain can track pharmaceuticals and medical supplies, ensuring they are authentic and have not been tampered with.
Real-World Example:
The integration of blockchain with Internet of Things (IoT) devices in healthcare has led to improved supply chain responsiveness. For instance, by monitoring the conditions of medical supplies in real-time, blockchain helps ensure that products are delivered safely and efficiently DelveInsight.
3. Enhancing Governance: Transparency and Accountability
Governments worldwide are exploring blockchain to enhance transparency, reduce corruption, and improve service delivery. By recording transactions on a public ledger, blockchain can make governmental processes more transparent and accountable.
Key Benefits:
- Transparent Voting Systems: Blockchain can create tamper-proof voting systems, ensuring election integrity.
- Efficient Public Services: Automation of processes like welfare distribution and licensing can reduce bureaucracy and improve service delivery.
- Reduced Corruption: The transparency of blockchain records makes it difficult to manipulate data, thereby reducing opportunities for corruption.
Real-World Example:
Estonia has implemented blockchain technology in various government services, including digital identities and e-residency programs. This has streamlined administrative processes and increased citizen trust in government operations Consensys – The Ethereum Company.
4. Overcoming Challenges: Scalability and Adoption
Despite its potential, the adoption of blockchain faces challenges such as scalability issues, regulatory uncertainties, and resistance to change. Addressing these challenges is crucial for widespread implementation.
Key Challenges:
- Scalability: As the number of transactions increases, blockchain networks can become congested, leading to delays and higher costs.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The lack of clear regulations can hinder investment and innovation in blockchain technologies.
- Resistance to Change: Organizations may be reluctant to adopt new technologies due to the costs and complexities involved.
Potential Solutions:
- Layer 2 Solutions: Technologies like the Lightning Network aim to improve blockchain scalability by processing transactions off the main chain.
- Clear Regulations: Governments can provide clear guidelines to foster innovation while ensuring security and compliance.
- Education and Training: Providing education and resources can help organizations understand the benefits and implementation strategies for blockchain.
5. The Future Outlook: A Decentralized World
The future of blockchain holds immense potential. As technology evolves, its applications are expected to expand, leading to more decentralized and efficient systems across various sectors.

Future Trends:
- Integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI): Combining blockchain with AI can lead to smarter contracts and automated decision-making processes.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Blockchain can track and verify sustainable practices in industries like agriculture and manufacturing.
- Global Standards: The development of global standards for blockchain can facilitate interoperability and widespread adoption.
Conclusion:
Blockchain technology is more than just the foundation of cryptocurrencies; it is a catalyst for change across industries. By enhancing transparency, security, and efficiency, blockchain is paving the way for a more decentralized and equitable future. As challenges are addressed and adoption increases, the transformative impact of blockchain will continue to unfold, reshaping the world as we know it.

Leave a Reply