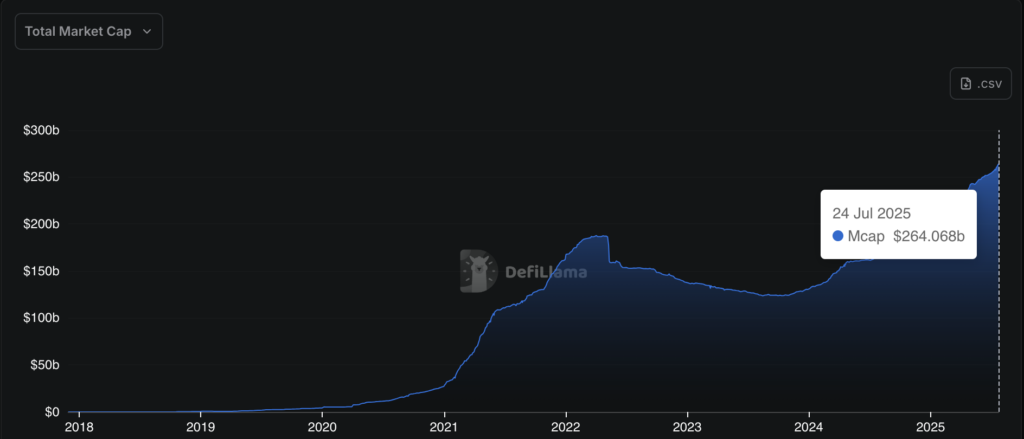
The US crypto industry is seeing a wave of renewed momentum following the passage of the GENIUS Act, a landmark law offering a clear legal framework for fiat-backed stablecoins. Within just a week of the Act being signed into law on July 18, nearly $4 billion flowed into the stablecoin sector, raising its total market capitalisation to over $264 billion.
This surge is more than just numbers. It marks a shift in confidence among investors, banks, and crypto firms. With legal uncertainty finally addressed, institutions are now free to enter the market without fear of sudden enforcement actions by regulators like the US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).

Coinbase CEO Brian Armstrong echoed this sentiment in an interview earlier this year, stating, “Everybody should be able to create stablecoins.” Now, that vision is rapidly becoming reality.
Understanding Stablecoin Types
Not all stablecoins are built the same. The GENIUS Act primarily focuses on fiat-backed stablecoins, which are tied 1:1 to a currency like the US dollar and backed by highly liquid reserves such as cash or US Treasurys. These stablecoins already dominate the market, accounting for 85% of the total supply.
Leading examples include:
- USDt (Tether)
- USDC (Circle)
Combined, these two alone have a market cap of over $227 billion. Under the new law, issuers of fiat-backed stablecoins must meet strict requirements, including full-reserve backing, independent audits, and licensing.
Other types of stablecoins include:
- Crypto-backed stablecoins: These use cryptocurrencies like ETH or tokenised Bitcoin as collateral. A notable example is DAI, which is overcollateralised and currently holds a market cap of around $4.35 billion.
- Algorithmic stablecoins: Designed to maintain their value via supply-and-demand algorithms, these proved unreliable, especially after the collapse of the Terra ecosystem. They are not covered under the GENIUS Act and will be regulated separately.
- Commodity-backed stablecoins: Tied to assets like gold, these are less common due to complex custody and lower liquidity. An example is Pax Gold (PAXG).
Wall Street and Banks Enter the Scene
The GENIUS Act has sparked immediate institutional action. On Tuesday, two major developments occurred:
- Anchorage Digital, the only federally chartered crypto bank in the US, partnered with Ethena Labs to launch a new issuance platform for USDtb, a fiat-backed stablecoin issued under the new regulatory framework.
- WisdomTree, a leading Wall Street asset manager, unveiled USDW, a dollar-pegged stablecoin designed to comply fully with GENIUS Act requirements. USDW also enables the creation of dividend-paying tokenised assets, blending stablecoins with traditional finance features.
Banks aren’t far behind. Days before the law was signed, Bank of America CEO Brian Moynihan confirmed the bank is exploring dollar-based stablecoin issuance. JPMorgan and Citigroup have also revealed plans to enter the stablecoin space, pending full compliance alignment.
Why This Matters for Crypto’s Future
The GENIUS Act doesn’t just impact stablecoins; it sets the tone for future crypto regulation. By establishing a clear and supportive framework, the law is bridging the gap between traditional finance and decentralised technologies.
The involvement of trusted names in banking and asset management could help reduce long-standing scepticism about crypto’s legitimacy and stability. It may also create more reliable options for cross-border payments, on-chain finance, and digital asset innovation.
While the focus remains on fiat-backed tokens for now, the Act opens doors for future regulatory models for other stablecoin types. With banks, fintechs, and crypto-native firms all eyeing the same opportunity, the competition is expected to drive faster innovation, safer products, and greater adoption.
In just one week, the GENIUS Act has reshaped the stablecoin landscape. With $4 billion in new capital and major institutions entering the space, the future of crypto is looking more regulated, inclusive, and institutionalised than ever before. The next phase will likely involve even broader adoption, stronger compliance infrastructure, and a deeper merging of Wall Street and Web3.

Leave a Reply